

Probabilities occur when an experiment is carried out and various results are possible. The set of the possible outcomes of an experiment is the sample space. An event is any subset of the sample space of an experiment
For example in the experiment "tossing a coin" there are two different outcomes: heads and tails. A head in this experiment is a specific event in our sample space.
Activities
1. Write down the sample space of the experiment of rolling two dice and consider the sum of the numbers on the top faces (using a tree diagram could be useful)


2. Graphic representations are useful to visualize the distribution of the data. They are also a good introduction to the probability distributions. This is an appropriated moment to introduce graphic representation of the data. Use a spreadsheet to make a graphic with your data from the sample space. Compare your graphic with your classmates' graphics.
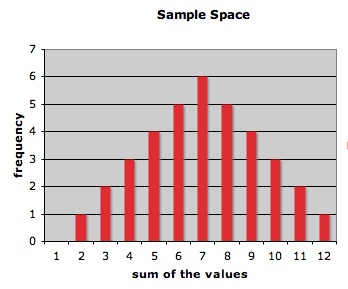
3. We already did the theoretical part. Now let us do the experimental part. Roll the dice 50 times and compare with the theoretical results.
4. Make a table with the results, make a histogram and compare with the histogram in part 2.
5. In the box 1 there are three marbles numbered from 1 to 3. In the box two there are three marbles number from 4 to 5. If we toss a coin and we get head, we choose a marble from the box 1, otherwise we choose a marble from box 2. Construct the sample space of this experiment.

References
Senk S. et al. (1998) Functions, Statistics
and Trigonometry. The University of Chicago School Mathematics
Project. Scott Foresman Addison Wesley.