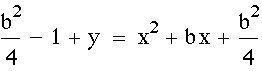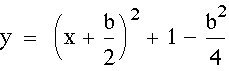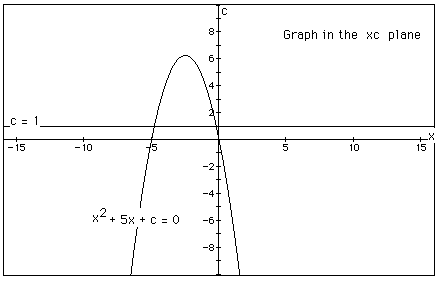EMAT 6680 Assignment 3
Some Different Ways to Examine
EMAT 6680 Assignment 3
Some Different Ways to Examine
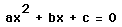 by
James W. Wilson and Paula Whitmire
University of Georgia
by
James W. Wilson and Paula Whitmire
University of Georgia
It has now become a rather standard exercise, with
availble technology, to construct graphs to consider the equation
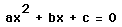 and to overlay several graphs of
and to overlay several graphs of
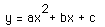 for different values of a, b, or c as the other two
are held constant. From these graphs discussion of the patterns
for the roots of
for different values of a, b, or c as the other two
are held constant. From these graphs discussion of the patterns
for the roots of
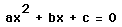 can be followed.
Let's observe the case of a= -3-purple, -2-red, -1
-blue, 0-green, 1- aqua, 2 - yellow, 3 -gray, and b=c=1. The following
graph is obtained.
All of the graphs go throught the point (0,1) as the
values of "a" changes. For negative values of "a",
the parabola points down and therefore has 2 real roots. The parabolas
with a positive "a" value all have a vertex above the
x-axis so have no real roots. For a=0, the graph is a line. It
appears that if the positive"a" parabolas were reflected
about y=1 then translated up and shifted to the right , they become
the graphs of the downward parabolas. The shift and translation
appear to be small as the absolute value of "a" gets
larger.
can be followed.
Let's observe the case of a= -3-purple, -2-red, -1
-blue, 0-green, 1- aqua, 2 - yellow, 3 -gray, and b=c=1. The following
graph is obtained.
All of the graphs go throught the point (0,1) as the
values of "a" changes. For negative values of "a",
the parabola points down and therefore has 2 real roots. The parabolas
with a positive "a" value all have a vertex above the
x-axis so have no real roots. For a=0, the graph is a line. It
appears that if the positive"a" parabolas were reflected
about y=1 then translated up and shifted to the right , they become
the graphs of the downward parabolas. The shift and translation
appear to be small as the absolute value of "a" gets
larger.
 For example, if we set
For example, if we set
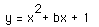 for b = -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, and overlay the graphs,
the following picture is obtained.
for b = -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, and overlay the graphs,
the following picture is obtained.
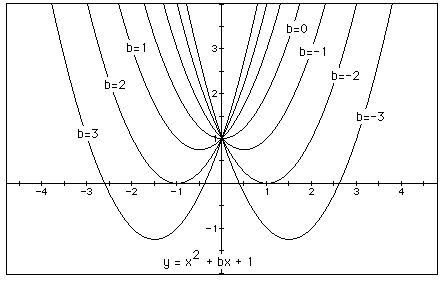 We can discuss the "movement" of a parabola
as b is changed. The parabola always passes through the same point
on the y-axis ( the point (0,1) with this
We can discuss the "movement" of a parabola
as b is changed. The parabola always passes through the same point
on the y-axis ( the point (0,1) with this
equation). For b < -2 the parabola will intersect the x-axis
in two points with positive x values (i.e. the original equation
will have two real roots, both
positive). For b = -2, the parabola is tangent to the x-axis and
so the original equation has one real and positive root at the
point of tangency. For -2 < b <
2, the parabola does not intersect the x-axis -- the original
equation has no real roots. Similarly for b = 2 the parabola is
tangent to the x-axis (one real
negative root) and for b > 2, the parabola intersets the x-axis
twice to show two negative real roots for each b.
Now consider the locus of the vertices of the set of
parabolas graphed from
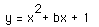 .
Show that the locus is the parabola
.
Show that the locus is the parabola
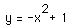
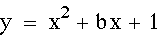
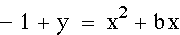
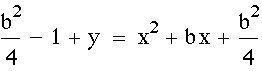
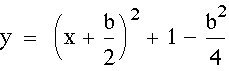 The locus of the parabolas is
The locus of the parabolas is
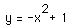 It is the downward parabola is the picture below.
It is the downward parabola is the picture below.
 Graphs in the xb plane.
Consider again the equation
Graphs in the xb plane.
Consider again the equation
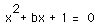 Now graph this relation in the xb plane. We get the
following graph.
Now graph this relation in the xb plane. We get the
following graph.
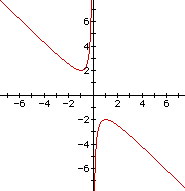 If we take any particular value of b, say b = 3, and
overlay this equation on the graph we add a line parallel to the
x-axis. If it intersects the curve in the xb
If we take any particular value of b, say b = 3, and
overlay this equation on the graph we add a line parallel to the
x-axis. If it intersects the curve in the xb
plane the intersection points correspond to the roots of the original
equation for that value of b. We have the following graph.
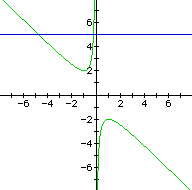 For each value of b we select, we get a horizontal
line. It is clear on a single graph that we get two negative real
roots of the original equation when b > 2,
For each value of b we select, we get a horizontal
line. It is clear on a single graph that we get two negative real
roots of the original equation when b > 2,
one negative real root when b = 2, no real roots for -2 < b
< 2, One positive real root when b = -2, and two positive real
roots when b < -2.
Consider the case when c = - 1 rather than + 1.
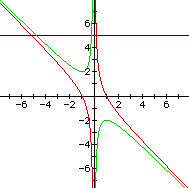 Graphs in the xc plane.
In the following example the equation
Graphs in the xc plane.
In the following example the equation
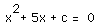 is considered. If the equation is graphed in the xc
plane, it is easy to see that the curve will be a parabola. For
each value of c considered, its graph will be
is considered. If the equation is graphed in the xc
plane, it is easy to see that the curve will be a parabola. For
each value of c considered, its graph will be
a line crossing the parabola in 0, 1, or 2 points -- the intersections
being at the roots of the orignal equation at that value of c.
In the graph, the graph of c =
1 is shown. The equation
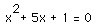 will have two negative roots -- approximately -0.2
and -4.8.
will have two negative roots -- approximately -0.2
and -4.8.
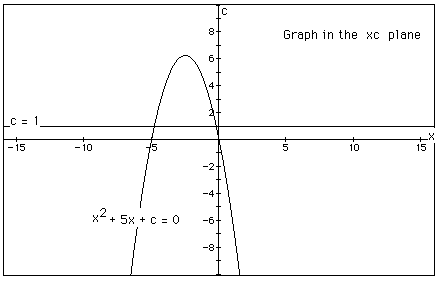 There is one value of c where the equation will have
only 1 real root -- at c = 6.25. For c > 6.25 the equation
will have no real roots and for c < 6.25 the
There is one value of c where the equation will have
only 1 real root -- at c = 6.25. For c > 6.25 the equation
will have no real roots and for c < 6.25 the
equation will have two roots, both negative for 0 < c <
6.25, one negative and one 0 when c = 0 and one negative and one
positive when c < 0.\
return