

Below is a picture of the construction. You will also see the measurements and calculations that I want to explore.
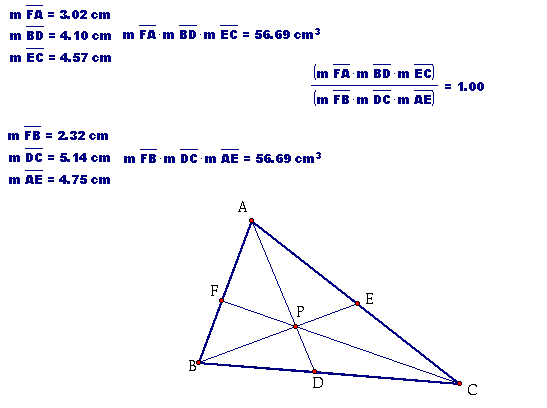
Click here to investigate on your own. Change the shape of the triangle and move P around inside triangle ABC. You will see that (AF)(BD)(EC) and (FB)(DC)(EA) will always be the same. Thus,
I am given the following:
Point P is on the inside of Triangle ABC
I want to prove that :
![]()
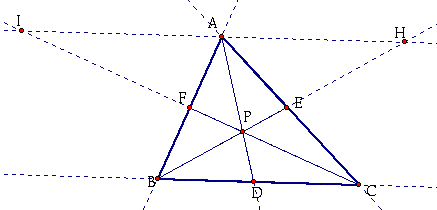
I will first construct some lines to help me begin my proof. I will extend all sides of the triangle ABC. I will also construct 3 rays with the endpoints at A, B, and C where all pass through P. Then, I will construct a line through point A and parallel to BC.
Consider the two yellow triangles:
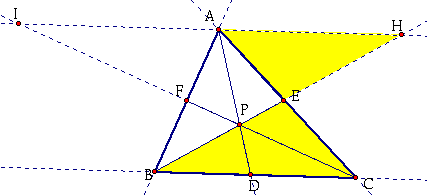
I know:
Angle(AEH) = Angle(CEB) because they are vertical angles
Angle(AHE) = Angle(CBE) because they are alternate interior angles
Angle(HAE) = Angle (BCE) because they are alternate interior angles
Therefore, Triangle(AEH) is similar toTriangle(CEB).
By CPCTC, ![]() .
.
Now, consider the two blue triangles below:
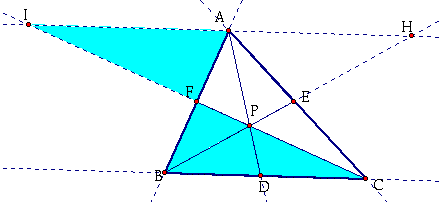
I know:
Angle(BFC) = Angle(AFI) because they are vertical angles.
Angle(FBC) = Angle(FAI) because they are alternate interior angles.
Angle(FCB) = Angle(FIA) because they are alternate interior angles.
Therefore, Triangle(FBC) is similar to Triangle(FAI).
By CPCTC, ![]() .
.
Next, consider the two orange triangles below:
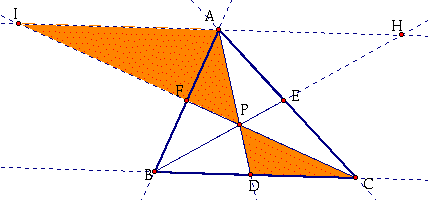
I know:
Angle(API) = Angle(DPC) because they are vertical angles.
Angle(PAI) = Angle(PDC) because they are alternate interior angles.
Angle(PIA) = Angle (PCD) because they are alternate interior angles.
Therefore, Triangle(API) is similar to Triangle(DPC).
By CPCTC, ![]() .
.
Finally, consider the two green triangles below:
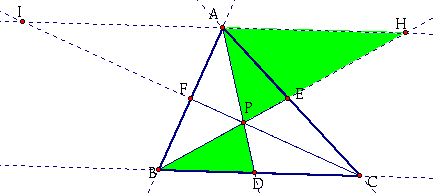
I know:
Angle(APH) = Angle(DPB) because they are vertical angles.
Angle(PAH) = Angle(PDB) because they are alternate interior angles.
Angle(PHA) = Angle(PBD) because they are alternate interior angles.
Therefore, Triangle(APH) is similar to Triangle(DPB).
By CPCTC, ![]() .
.
So, here is a short recap:
Now, we need to apply some simple algebra.
From the first equation, I can get:
From the second equation, I can get:
From the third and fourth equations, I get:
Now, by substitution,
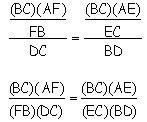
Cross multiply
Cancel (BC)
And finally...
Click here to explore with a GSP sketch of this construction. Notice the ratio of the area of triangle ABC to the area of triangle EFG. It is always greater than or equal to 4.
The ratio of the area of triangle ABC to the area of triangle EFG is equal to 4 iff P is the centroid.
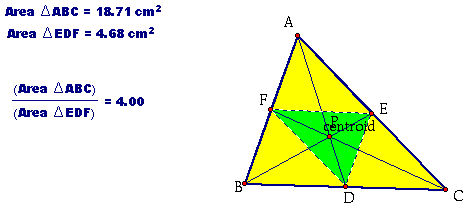
Click here to play around with this construction.