 By Page Bird
A Triangle in a Rectangle
A triangle has two shared vertices
and one shared side with a rectangle. The third vertex is anywhere
on the side opposite of the shared side.
By Page Bird
A Triangle in a Rectangle
A triangle has two shared vertices
and one shared side with a rectangle. The third vertex is anywhere
on the side opposite of the shared side.
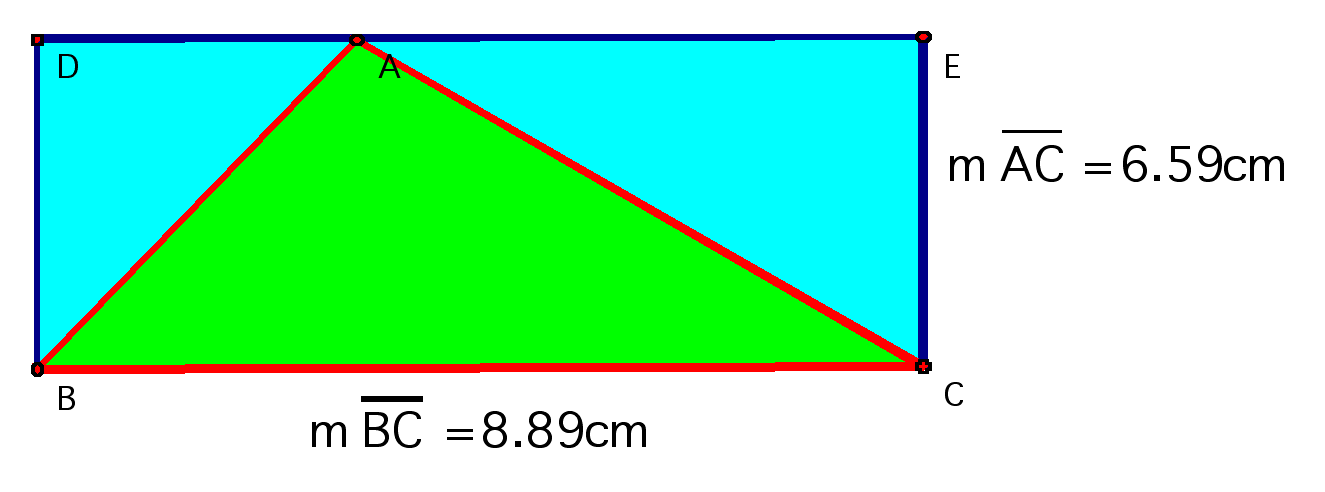 How does the area of the triangle compare
with the area of the rectangle? Why do you think this relationship
holds?
This relationship always holds because
the base and the height of the triangle stay the same regardless
of where the third vertex lies on the rectangle.
So at all times the base of the given
triangle is the same and the height of the triangle is also the
same. The triangle will always have a 1-to-2 ratio with the rectangle.
How does the area of the triangle compare
with the area of the rectangle? Why do you think this relationship
holds?
This relationship always holds because
the base and the height of the triangle stay the same regardless
of where the third vertex lies on the rectangle.
So at all times the base of the given
triangle is the same and the height of the triangle is also the
same. The triangle will always have a 1-to-2 ratio with the rectangle.

Click here
to see a GSP sketch.
Click here to return
to my Emat 6690 page.



