The following is an investigation of the quadratic
function, generally of the form ![]() and
the nature of the roots of the equation
and
the nature of the roots of the equation ![]() .
.
Consider the graph of ![]() for -3 < b < 3. From the overlay of graphs, the following
picture is obtained:
for -3 < b < 3. From the overlay of graphs, the following
picture is obtained:
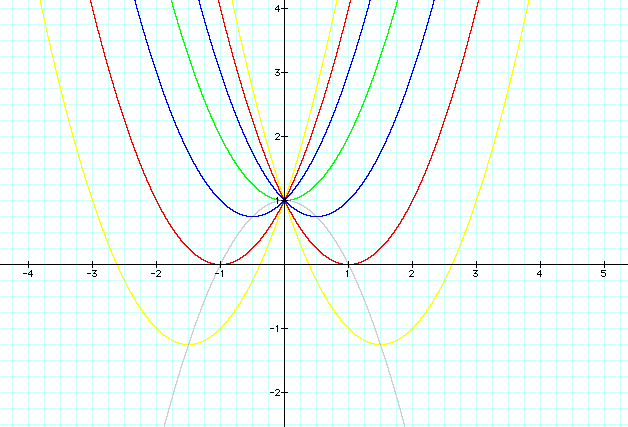
As the b value is changed, the parabola "moves"
through the coordinate system. All of the curves have the same
y-intercept (the point (0, 1), however the number of real
roots is not. For b < -2 and b > 2, the quadratic has two
real roots (it intersects the x-axis twice); for b = -2 and b
= 2, the graph is tangent to the x-axis, so it has one real root;
and for -2 < b < 2, the graph does not intersect the x-axis,
therefore there are no real roots. The locus of vertices forms
the parabola ![]() . More generally, the locus of
vertices for a family of parabolas will take the form
. More generally, the locus of
vertices for a family of parabolas will take the form ![]() when
a=-1 or
when
a=-1 or ![]() when a = 1.
when a = 1.
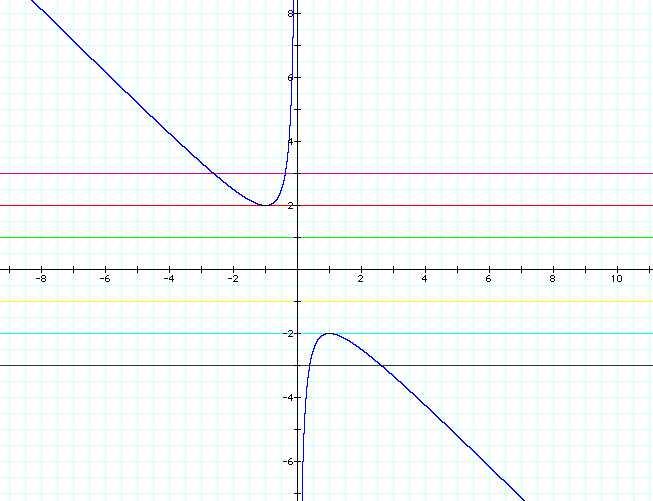
Consider once again the equation ![]() .
If we solve for b,
.
If we solve for b,
and the following relation is obtained in the xy-plane if y = b:
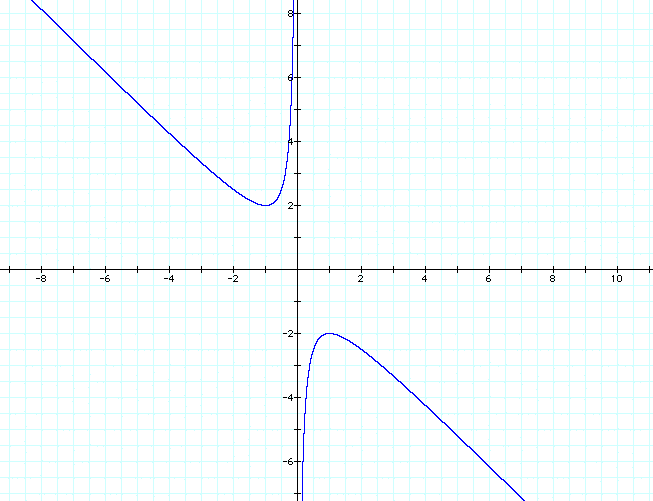
If we overlay the equations of any particular value of b, (for instance b = 2), we would get a horizontal line. The points of intersection represent the real roots of the equation. There are no points of intersection for the -2 < b < 2, therefore there are no real roots for the quadratic as stated earlier: