

The contents of this page are an investigation into the behavior and characteristics of pedal triangles under various conditions. Pedal triangles are constructed by selecting an arbitrary point on the plane, then constructing the perpendicular lines from that point to the extensions of the sides of a triangle and finally connecting the intersection points of the perpendicular lines and the extended sides of the triangle with segments. This is illustrated below.
NOTE: The animations that are linked to from this page all require that Geometer's Sketchpad be installed and that your web browser recognizes files with suffix .gss or .gsp as being Geometer's Sketchpad files.
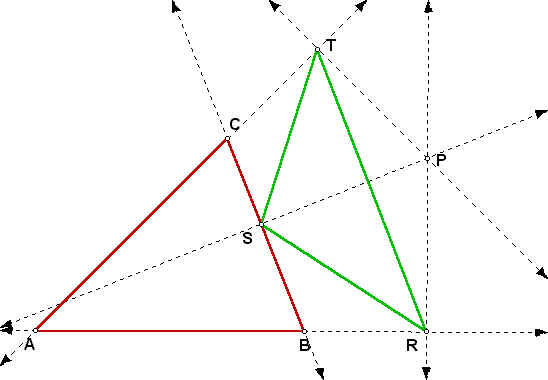
Triangle RST is the pedal triangle to Triangle ABC constructed from point P. For a Geometer's Sketch Pad script that will construct the pedal triangle for an arbitrary triangle ABC and an arbitrary point P click here.
Several specific pedal triangles to a given triangle can be constructed by letting point P be specific points related to the given triangle. For instance, we could use the centroid, the orthocenter, the center of the incircle, the center of the circumcircle or the center of one of the excircles as point P. Let's look at some of these.
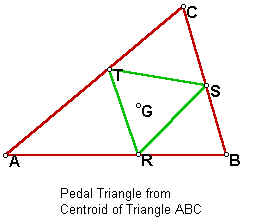
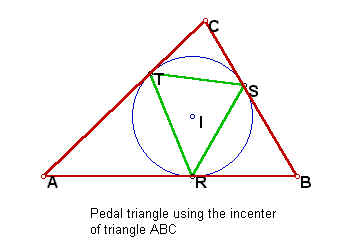
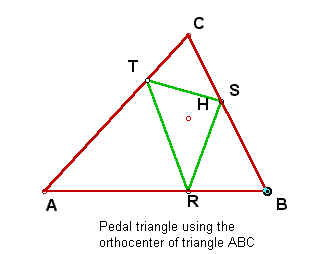
What if triangle ABC is such that the orthocenter H is located outside of the triangle?
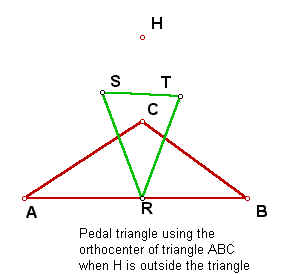
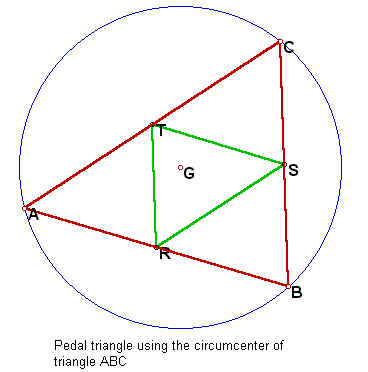
These pedal triangles are not very interesting in themselves. However, some of them do display some interesting behavior if we do a little animation and watch what happens as we trace certain points.
Pedal Point on an Excircle of Triangle ABC
To see a Geometer's Sketch Pad animation of the traces of the midpoints of the sides of the pedal triangle when a point on one of the excircles of a triangle is used to construct the pedal triangle click here.
The midpoints of the sides trace what appear to be ellipses. One ellipse has its major axis aligned with the bisector of the angle of the vertex that the center of the excircle lies upon. The other two ellipses have their minor axes aligned on the bisectors of the angles of the extended sides and the included side that is tangent to the excircle.
Simpson Line
Under certain conditions the sides of the pedal
triangle are colinear. That is, the pedal triangle is a
degenerate triangle. Some investigation using Geometer's
sketch pad will show that this happens anytime the pedal point
is on the circumcircle of the triangle. This line segment
is called the simpson line. An interesting exercise is to
extend the simpson line and trace it as the pedal point is moved
around the circumcircle. To see this animation click
here.
Traces done by animation
The pattern traced is very pleasing to the eye, isn't it?. What if we do the same type of animation with the extended sides of pedal triangles around various circular paths?
Click here to see what happens when the pedal point is moved around a circle whose center is the center of the circumcircle but with a lesser diameter.
A more symmetric and more pleasing to the eye
trace can be made if the pedal point is animated about the incircle
of triangle ABC. Click here to
see this.
There are, of course, many more investigations
that can be done involving pedal triangles. I hope that
the ones presented above will motivate you to go further.
RETURN