Green Pinwheel
2222
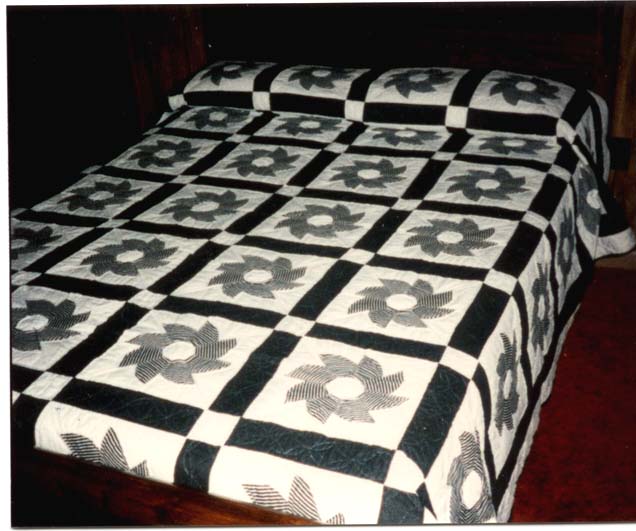

Analysis of Green Pinwheel

KEY:
1) red segments represent reflection mirrors
2) light green segments represent glide mirrors that are not reflection mirrors
3) dark blue segments represent translation generators
4) dark green segments represent shortest glide vectors that are not translation
generators
5) yellow points represent cyclic centers
6) light blue points represent dihedral centers
7) fundamental region is shaded pink
8) quilt block is shaded yellow
Symmetries present:
rotation, translation
Description of symmetries: There
are no reflection mirrors.There are 2-fold cyclic rotation centers located
at the centers of the star shapes and in the center of the green horizontal
and vertical strips, as well as in the center of the small white squares.
The shortest translation vectors horizontally and vertically are the distance
between the centers of the stars.
Description of fundamental region:
A rectangle that has 2-fold centers for vertices
and at the midpoints of the longest sides.
Description of symmetries in block:
Looking at an individual star within a block, we have cyclic 8-fold symmetry.
Relationship between block and fundamental region:
The area of a block is twice the area of the fundamental region.
Description of symmetries in quilting:
The quilter 'traced' the pattern of the quilt embellishing
with a strip pattern in the green strips. Thus, the quilting symmetry is not
in harmony with the quilt symmetry. To see an analysis of this strip pattern,
see below.
Green Pinwheel Border Pattern
To see entire quilt, scroll up to the top.
TRVHG or *22i
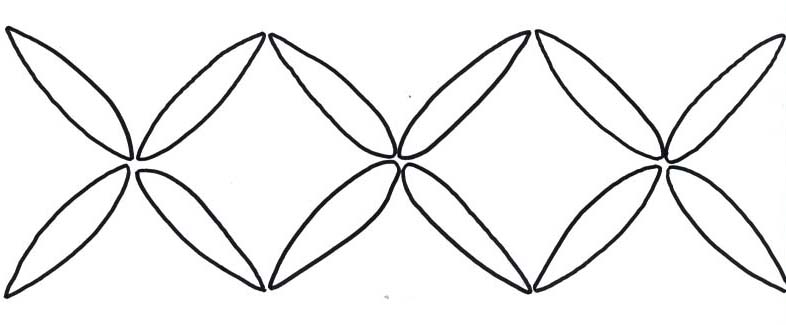
Analysis of hand-quilted border
Note that this stitching occurs in the dark green strips
throughout the quilt.
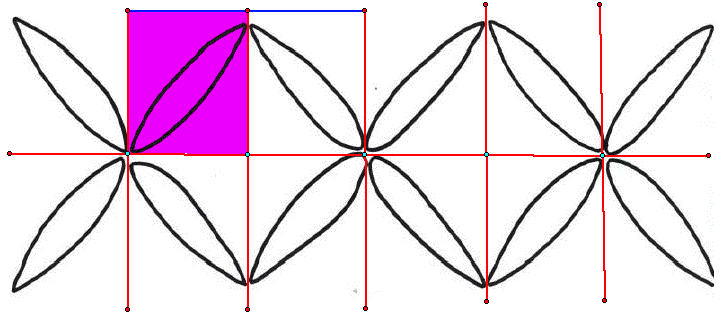
Analysis of border pattern (made from stitching)
There are vertical mirrors and the center line
is a horizontal mirror (and therefore a glide mirror.)
The translation vector of the strip pattern is equal to the distance from
the center of one star to the center of the next star.This vector is also
the glide vector. There are 2-fold dihedral centers at the intersection of
the mirrors. The fundamental region is a rectangle that has mirrors on three
sides (includes basically one-fourth of the star figure.)



