Polar Equations
By: Diana Brown
(1) Investigate
![]()
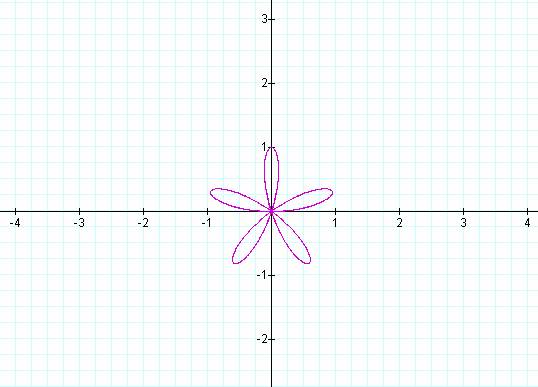
When a
and b are equal (in this case a and b both equal one), and k is an integer,
this is one textbook version of the “ n-leaf rose.”
K = 1 K = 2
K = 3 K = 4
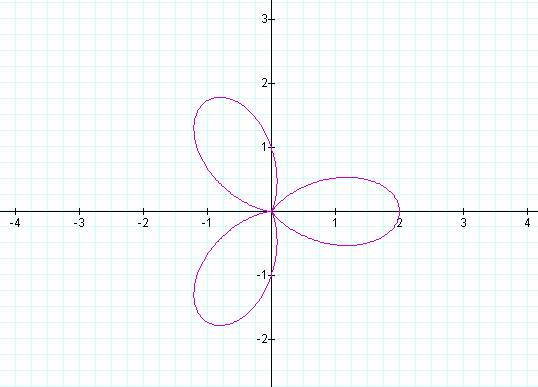
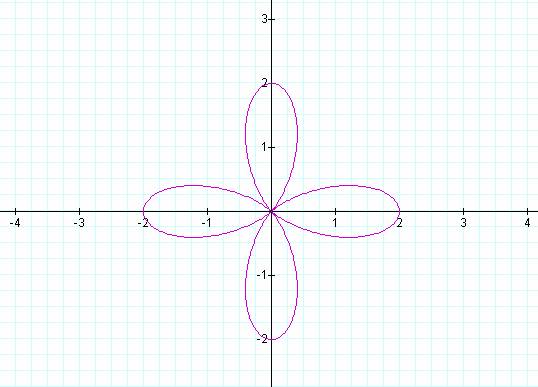
K = 5 K = 6
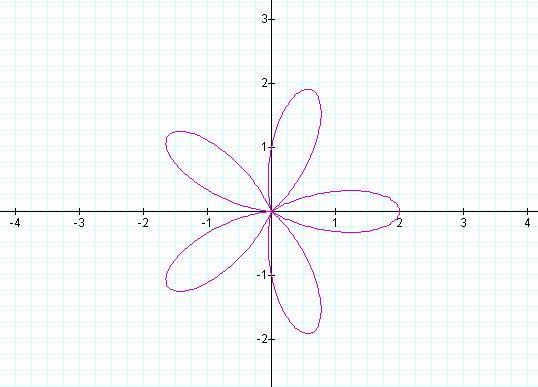
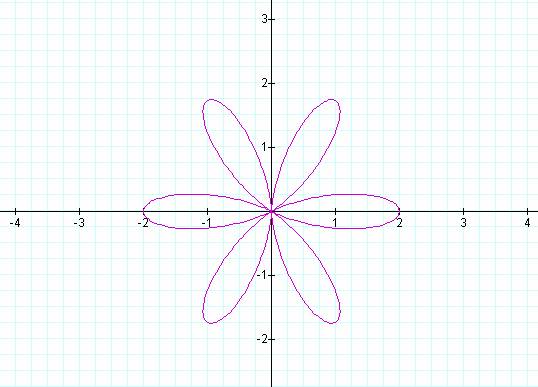
K = 7 K = 8
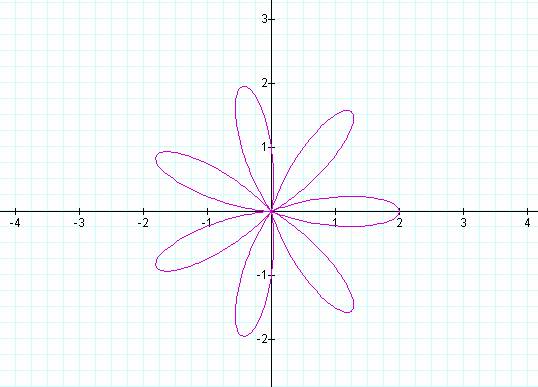
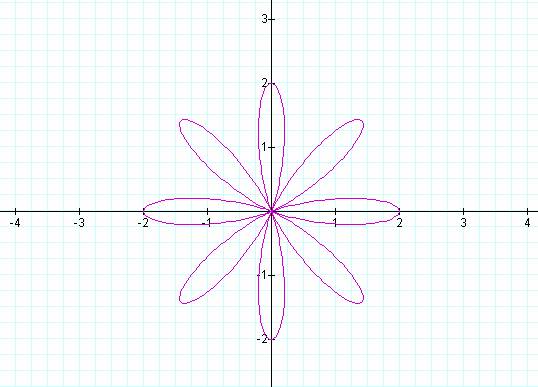
K = 9 K = 10
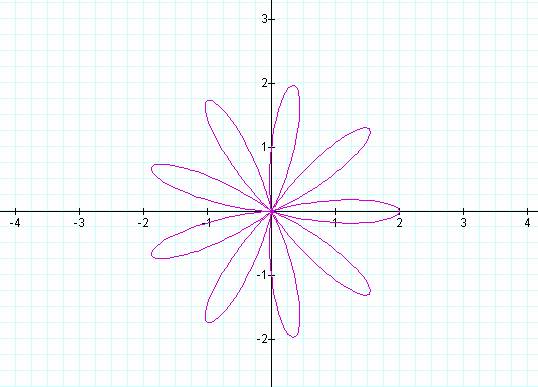
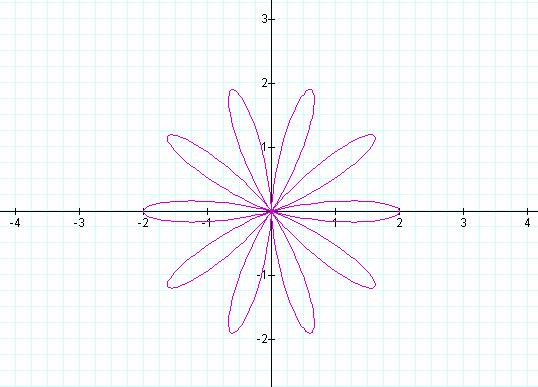
Notice that k determines the number of “leaves/pedals” on
the “rose.”
Click here to open a Graphing
Calculator file to animate the graph as k varies.
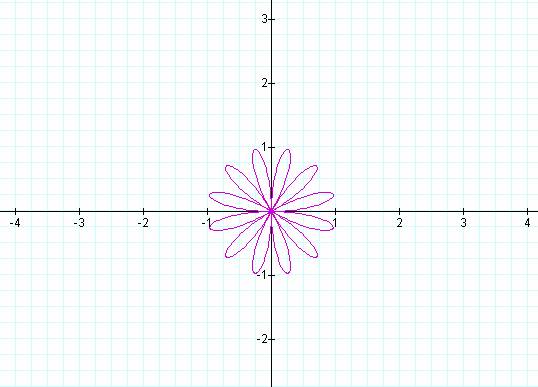
(2) Investigate and compare
![]()
for various k.
K = 3 K
= 4
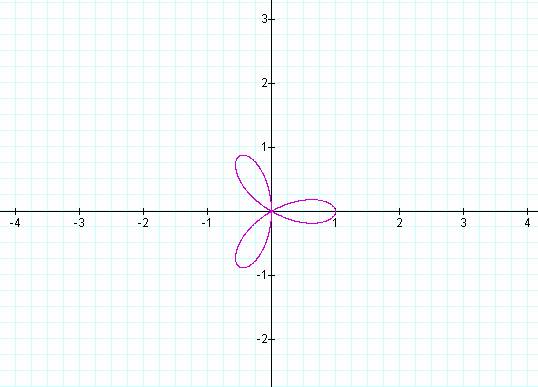
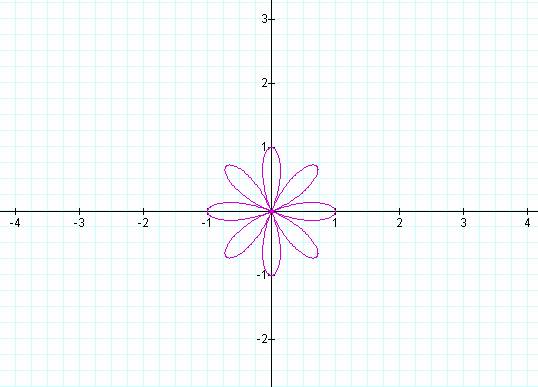
K = 5 K
= 6
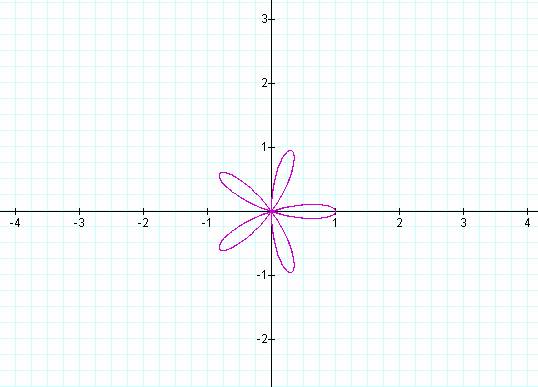
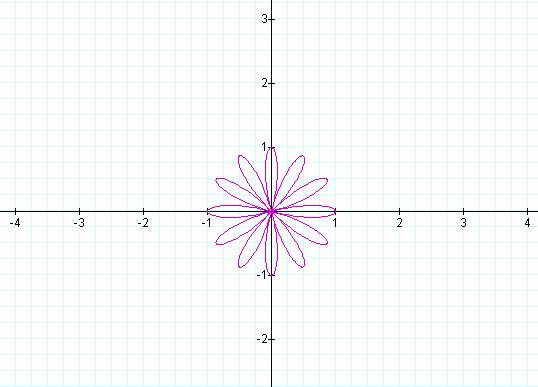
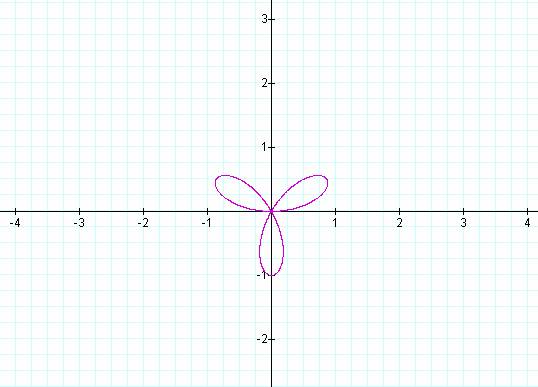
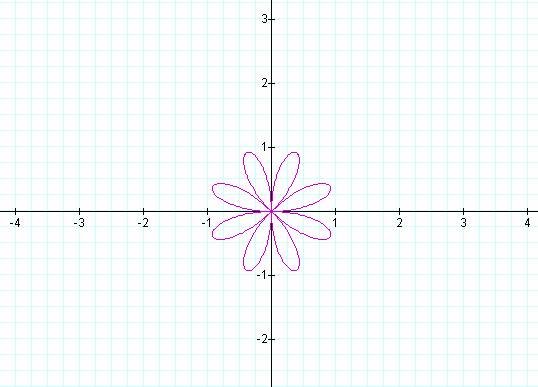
Notice that if k is odd then the number of pedals is equal
to k, but if k is even then the number of pedals is 2k.
(3) Investigate the same equation as # 2, but replace
cosine with sine.
K = 3 K
= 4
K = 5 K
= 6