Investigate

When a and b are equal, the graph is like the following(a=b=2)
according to k=1, k=2, k=3, k=4.



 To explore Click here
To explore Click here
When a=b=2, the graph pass through
(4,0) and (0,0) regardless of the
value of k.
If k is
odd then the graph meets at 2 and
-2 with y-axis and if k is even
then it does at 4 and -4 with x-axis.
The number of leaves is the value of
k.
What if the values of a and
b are different?
Case of a>b.
Let's see the case of a=2 and b=1(k=1, 2, 3,4).



 Case of a<b.
Let's see the case of a=1 and b=2(k=1, 2, 3,4).
Case of a<b.
Let's see the case of a=1 and b=2(k=1, 2, 3,4).




First observation
If a is bigger than b then the figure becomes
to a circle as the difference is bigger regardless of k.
To explore Click here
If b is bigger than a then new leaves
appear and the size of new ones is difference of a and b. To explore
Click here
If  then the graph is like the following(b=2)
according to k=1, k=2, k=3, k=4.
then the graph is like the following(b=2)
according to k=1, k=2, k=3, k=4.



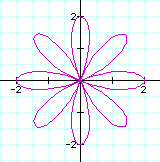
When b=2, the graph pass through
(2,0) and (0,0) regardless of the
value of k.
If k is even then it does at 2 and -2 with y-axis and x-axis.
If k is odd
then the number of leaves is the value of
k and if k is even then it is twice value of k.
What if cosine function is
changed to sine function?
In fact, we can expect a rotation
since sine function with addition of 90 degree becomes cosine
function.
The followings are graphs of when a=2, b=2, and k=1, 2, 3, 4.
when a=2, b=2, and k=1, 2, 3, 4.




Second observation
The graph of  is some degree rotation
of
is some degree rotation
of  .
The rotation degree is decreasing as k is increasing.
.
The rotation degree is decreasing as k is increasing.
Return to
Hyungsook's homepage












![]() then the graph is like the following(b=2)
according to k=1, k=2, k=3, k=4.
then the graph is like the following(b=2)
according to k=1, k=2, k=3, k=4.






