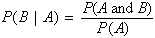 .
.Conditional Probability: the probability of event B given that event A occurs. This is represented by P(B | A). In other words, this is the probability that two events occur together. This is calculated by: P(A and B) = P(A)P(B | A).
For three events A, B and C, if each event has the condition that all of the previous events must occur, then
P(A and B and C) = P(A)P(B | A)P(C | A and B).
Conditional Probability: When P(A) > 0, the conditional probability of B given A is
P(B | A). In other words, this is the probability that two events occur together. This is calculated by:
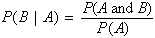 .
.
Independent Events: Two events A and B are independent if P(B | A) = P(B).